It has always been an endeavor of the School of Engineering & Sushant University Gurgaon to explore possibilities of helping the society and creating an atmosphere of corporate-social responsibility. Besides the learned professors who are ever involved in the areas of research, the university encourages students as well.
This article has been prepared by one of the students of the college who has done a research on an aspect of human life that seems to be working as slow poison.
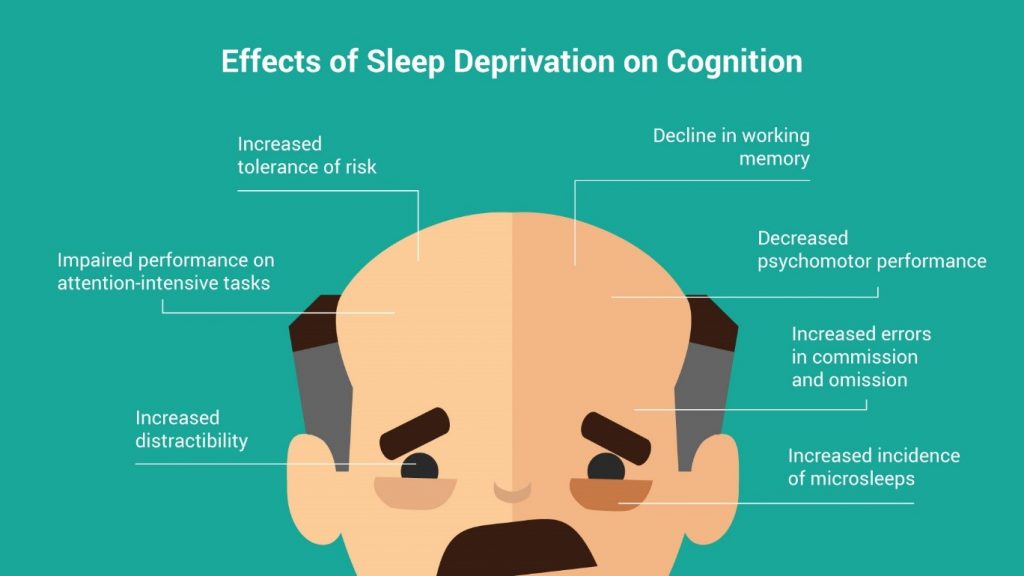
Almost everyone has faced sleep deprivation at one point or another in their lives. The term “sleep deprivation” generally refers to a state caused by inadequate quantity or quality of sleep, including voluntary or involuntary sleeplessness. Sleep deprivation is a common practice in modern society, but its effects on cognitive performance are only beginning to be understood from a scientific perspective.
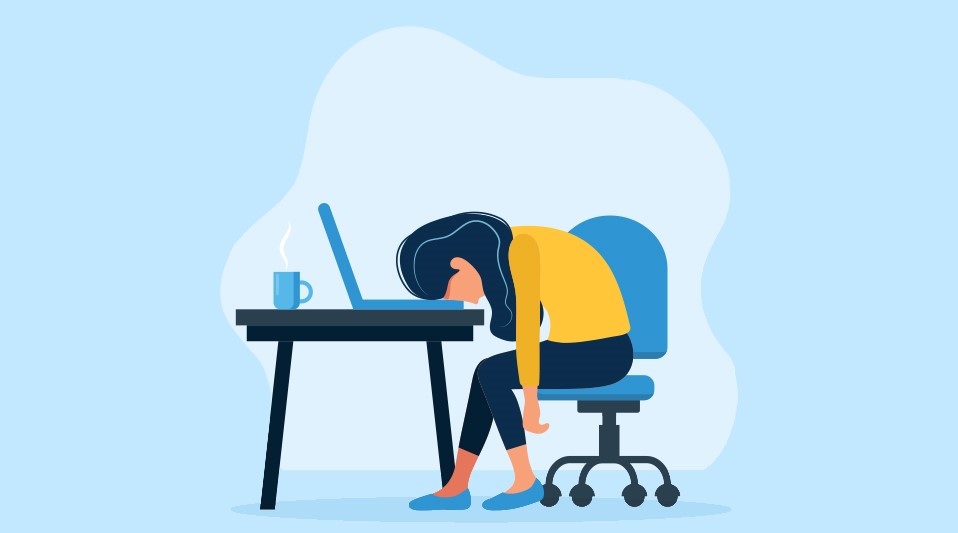

Not getting enough sleep will disturb our ability to process emotional component of information properly. This can impact our ability to learn from mistakes because the normal method of processing emotional memory is jeopardized.
Similarly, our creativity is also harmed by sleep deprivation. As a result, sleep deprived individuals often read a sentence a few times to understand the meaning. This can be damaging for our creativity as the brain has difficulty generating and remembering new ideas.
There are many other effects of sleep deprivation on our cognitive performance, for example a person suffering from migraine may be more prone to having a headache in the day due to less sleep. Mental health issues like anxiety and depression may also be affected due to it.
Lack of sleep and sleep disorders can contribute to the symptoms of depression.
The most common sleep disorder, insomnia, has the strongest link to depression. In a study conducted in 2007 it was found that, those with insomnia were five times more likely to develop depression as those without.
Research has found that sleep helps the brain can get rid of threatening substances like beta amyloid proteins. In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that collect between neurons and disrupt cell function. It has been found that sleep deprivation increases beta quantity of beta amyloid in the brain.
By getting proper sleep we can help the brain recover and steer clear of many negative results of poor sleep. Many researchers state that a good sleep maybe a good way of preventing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Although, more studies are needed to definitively determine the role of sleep in precluding cognitive decline, early research suggests that developing a better sleep schedule may lower the long term chances of developing Alzheimer
While not getting sufficient hours of sleep can lead to astronomical short or long term side-effects, many studies have found that a lack of sleep is not the only problem. Too much sleep is also associated with cognitive decline.
Therefore, it is an important reminder that a healthy sleep involves both a minimum and a maximum.
There are many ways to improve quality sleep, including counseling, lifestyle and environmental adjustments, medications, and alternative therapies. By improving our every day habits and routines, we can get rid of many complication of getting a poor sleep. We can set a bedtime for ourselves or schedule our day accordingly to incorporate a better sleep schedule. We should steer clear from alcohol and caffeine in the evening, and try to reduce our electronics in the bedroom. These are a few examples to improve our sleep hygiene and get a proper night’s rest.

Angelina
Ist year student (B.Tech-AI & ML)
School of Engineering and Technology
Sushant University
