Education is facilitating learning and acquiring the values, skills, morals and personality development. There are many methods of getting the right education like story-telling, teaching, training, discussion and research. It helps the student to develop its critical thinking towards a search and bringing out new paradigms in it. It motivates the student to ask questions, to analyze the situations from critical angles, to develop new theories and to make this world a better place.
According to Peter Facione (2011), Critical Thinking is the purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgment is based. By definition, it seems to be very technical but the term was simplified by Benjamin Bloom in 1965 by introducing Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Concept of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist, undertook a project of classifying learning behavior in 1956. He along with his researched various factors like intellectual, emotional, physical and behavioural skills and were able to identify six levels of cognitive performance, namely, knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. These levels were then simplified into six activities for students, namely, remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating. These levels and activities helped the teacher as well students to analyze the situation from different angles and bring out the comprehensive and critical solutions. The framework is so powerful that it can be applied to any content created for students
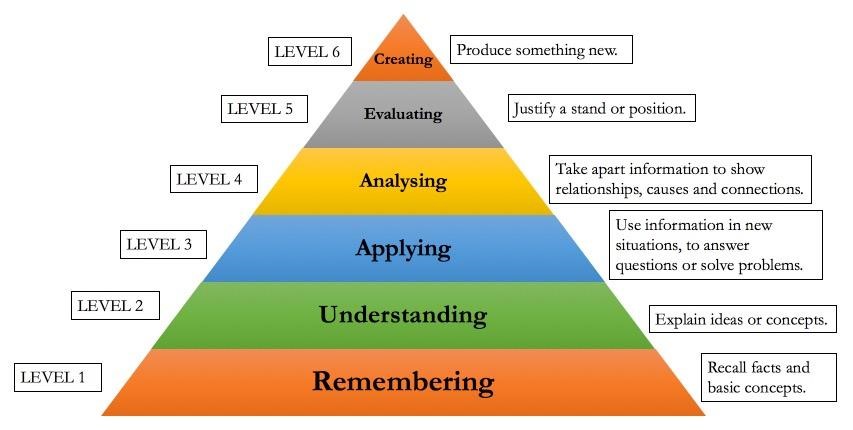
Bloom’s Taxonomy for Teachers
For Teachers, Bloom’s Taxonomy is like a common language to discuss learning and assessment methods. It helps in encouraging high-order thoughts among students by mapping the activities and assessment criteria to Learning Outcomes. Learning Outcomes become the goals and the curriculum is divided and are spread into various activities, experiences and exercises. It also acts as a checklist to ensure all levels of domain are assessed and aligned in a proper manner. Sushant University, one of the top private universities in Delhi-NCR implements Bloom’s Taxonomy to evaluate the learning outcome of its students.
Bloom’s Taxonomy for students
For students, this framework challenges them to unfold the hidden ideas behind each concept. According to Alford, Herbert and Fragenheim (2006), teachers ask 300 – 400 questions a day. As such, it is mandatory for teachers to have so many activities and exercises ready with them to engage students to have more discussion; stimulate higher cognitive thinking as well as evaluate the learning progress of the students. Bloom’s taxonomy helps the students to bring justification to their answers, search for various related content, question the solutions, search for new ideas and reflect in a creative manner. It prompts them to dig deep into the concept and work themselves in answering the justification behind selecting an answer for the question being asked. To summarize, Bloom’s taxonomy helps teachers to encourage and teach students who are struggling with finding other ways of thinking to make their own decisions not just in a classroom but also in promoting a more creative life skill.
References
- Facione, Peter A. (2011). “Critical Thinking: What It is and Why It Counts”. insightassessment.com. p. 26.
- Alford, G., Herbert, P., & Frangenheim, E. (2006). Bloom’s Taxonomy Overview. Innovative Teachers Companion , 176 – 224. ITC Publications
